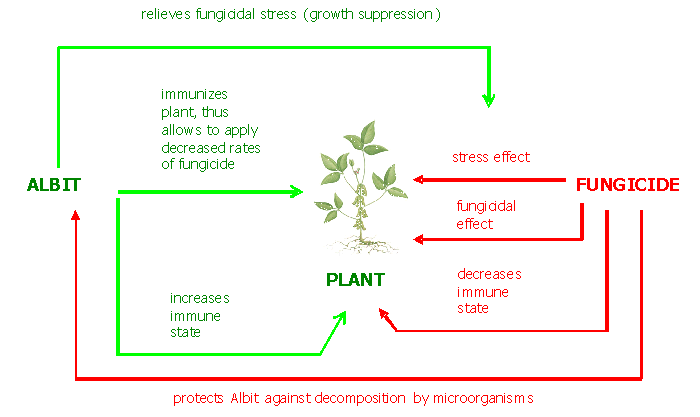
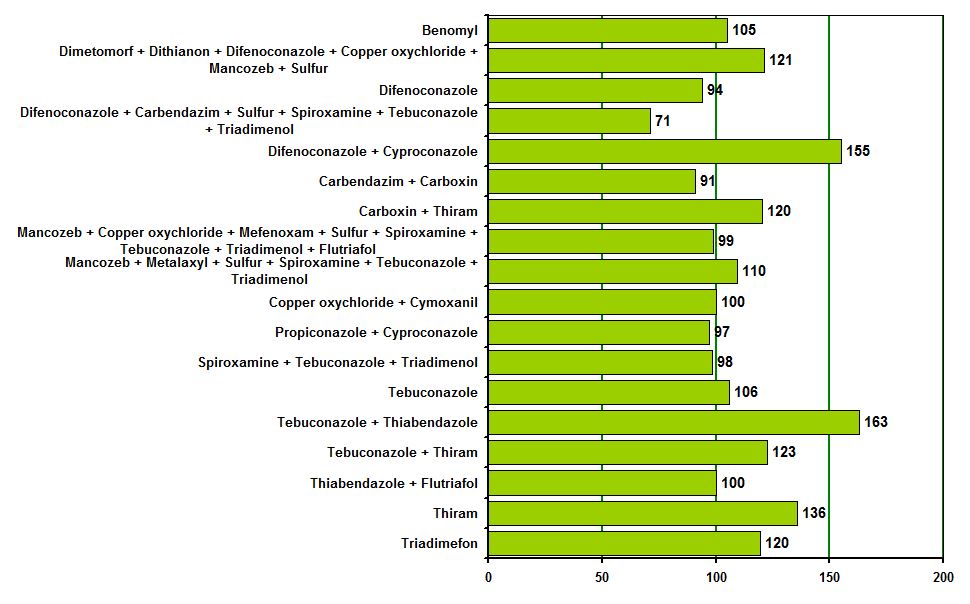
Summarized data of multiple (252) field trials which were carried out through
1999-2006, demonstrated high efficiency of joint application of biostimulant
Albit with halved (decreased) rates of chemical fungicides and protectants
based on mancozeb, dimethomorph, propiconazole, cyproconazole, triadimefon,
thiabendazole, tebuconazole, flutriafol, carboxin, thiram, difenoconazole,
carbendazim, sulphur, mancozeb, metalaxyl, copper compounds, oxadixyl, cymoxanil,
epoxiconazole, mefenoxam, spiroxamine, triadimenol, benomyl, etc.
(Table 13, Fig. 1).
Albit was combined both with fungicides used for presowing seed treatment
(based on difenoconazole, carboxin, thiram, etc.) and with ones used for foliar
spraying (based on propiconazole, cyproconazole, epoxiconazole, carbendazim,
etc). Effectiveness of mixtures of Albit and fungicides was demonstrated for
wide range of diseases (internal, soil, leaf infections, bacterial and seed
infections) of different agricultures: vine, potatoe, flax, sunflower, millet,
winter and spring wheat, barley, sugar beet, soybean, apple. Infection levels
varied from low (prevalence of 2-10% in trials of All-Russia Institute of Vegetable
Selection and Seed Breeding on soybean) to artificially high (92-95% in trials
of All-Russia Institute of Leguminous and Groat Crops on millet). There
was no cases of incompatability or decreased efficiency of fungicides used
in combination with Albit. These facts are witness of Albit/fungicide
combination universality (Table 13).
Fig. 1. Biological efficacy of tank mix Albit + 1/2 fungicide, % from
efficacy of full fungicide dose
Trial results persuasively show advantages of Albit/fungicide combinations. It is necessary
to note, that in the last years, 74 trials studying this phenomenon were carried out.
Results of all conducted experiments on combination of Albit with decreased application
rates of fungicides are presented in summarizing table (Table 13).
In this table you can see agricultural (influence on yield), biological
(fungicidal) and economical (net profit obtained from one hectare) effectiveness
of these combinations.
| Nr |
Active ingredients
of the fungicides used in the experiment |
Application rate of
the fungicide |
Application rate of
Albit |
Crop |
Disease |
Biological Efficiency ,% |
Yield, centners/hectare |
Net profit, USD/hectare |
Efficiency of decreased
rate of fungicide + Albit in comparison to the efficiency full rate, % |
Comments |
Institution, year |
| full |
decreased |
full rate |
decreased rate + Albit |
full rate |
decreased rate + Albit |
full rate |
decreased rate + Albit |
regarding to disease control |
regarding to yield increase |
| 1. |
tebuconazole |
0.5 L/tonne |
0,25 L/tonne |
30 g/tonne |
spring barley |
root rots |
57 |
43 |
21.4 |
13.2 |
- |
- |
75 |
62 |
Yield in control was 7.7 centners/hectare. |
Kostroma regional plant protection station,
2006 |
| 2. |
tebuconazole |
0.5 L/tonne |
0,25 L/tonne |
30 g/tonne |
spring barley |
root rots |
57 |
43 |
24 |
17.4 |
- |
- |
75 |
73 |
Foliar spraying with Albit, 30 ml/hectare
was carried out. Yield in control was 11.0 centners/hectare. |
Kostroma regional plant protection station,
2006 |
| 3. |
tebuconazole |
0.5 L/tonne |
0,25 L/tonne |
30 g/tonne |
spring barley |
net blotch |
39 |
44 |
21.4 |
13.2 |
- |
- |
113 |
62 |
BE against net blotch is indicated for
EC stages 20-29. Yield in control was 7.7 centners/hectare. |
Kostroma regional plant protection station,
2006 |
| 4. |
tebuconazole |
0.5 L/tonne |
0,25 L/tonne |
30 g/tonne |
spring barley |
net blotch |
40 |
65 |
21.4 |
13.2 |
- |
- |
163 |
62 |
BE against net blotch is indicated for
EC stages 50-69. Yield in control was 7.7 centners/hectare. |
Kostroma regional plant protection station,
2006 |
| 5. |
tebuconazol e |
0.5 L/tonne |
0,25 L/tonne |
30 g/tonne |
spring barley |
net blotch |
39 |
44 |
24 |
17.4 |
- |
- |
113 |
73 |
Foliar spraying with Albit, 30 ml/hectare,
was carried out. BE against net blotch is indicated for EC stages 20-29.
Yield in control was 11.0 centners/hectare. |
Kostroma regional plant protection station,
2006 |
| 6. |
tebuconazole |
0.5 L/tonne |
0,25 L/tonne |
30 g/tonne |
spring barley |
net blotch |
55 |
69 |
24 |
17.4 |
- |
- |
125 |
73 |
Foliar spraying with Albit, 30 ml/hectare
was carried out. BE against net blotch is indicated for EC stages 50-69.
Yield in control was 11.0 centners/hectare. |
Kostroma regional plant protection station,
2006 |
| 7. |
propiconazole + cyproconazole |
0.4 L/hectare |
0,2 L/hectare |
40 ml/hectare |
winter wheat |
brown rust and other rusts |
90 |
86 |
53.8 |
54.2 |
- |
- |
96 |
101 |
BE of halved dose of Alto-super (without
Albit) was 47-58%, yield increase – 9.5%. Yield in control was 45.4 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Institute of Biological Plant
Protection, 2004 |
| 8. |
propiconazole + cyproconazole |
0.4 L/hectare |
0,2 L/hectare |
40 ml/hectare |
winter wheat |
Septoria leaf
spot s and other spots |
79 |
78 |
53.8 |
54.2 |
- |
- |
99 |
101 |
BE of halved dose of Alto-super (without
Albit) was 47-58%, yield increase – 9.5%. Yield in control was 45.4 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Institute of Biological Plant
Protection, 2004 |
| 9. |
cyproconazole |
– |
0,1 L/hectare |
30 ml/hectare |
sugar beet |
– |
– |
– |
– |
347 |
- |
- |
– |
– |
Alto was applied in combination with second
foliar spraying with Albit. Yield in control was 241 centners/hectare. |
Chapaev breeding farm OSC, 2003 |
| 10. |
cyproconazole |
– |
0,1 L/hectare |
30 ml/hectare |
sugar beet |
– |
– |
– |
– |
360 |
- |
- |
– |
– |
Alto was applied in combination with second
foliar spraying with Albit. Yield in control was 273 centners/hectare. |
Chapaev breeding farm OSC, 2003 |
| 11. |
propiconazole |
0.5 L/hectare |
0,35 L/hectare |
40 ml/hectare |
winter wheat |
– |
– |
– |
53 |
58.8 |
0 |
55,68 |
– |
111 |
Trial on wheat var. Yermak. Presowing
treatment with full dose of fungicide – tebuconazole 0.5 L/tonne; with
reduced dose of fungicide – tebuconazole 0.35 L/tonne + Albit 40 ml/tonne. |
Ulyanovets LLC, 2005 |
| 12. |
propiconazole |
0.5 L/hectare |
0,35 L/hectare |
40 ml/hectare |
winter wheat |
– |
– |
– |
52.8 |
53.2 |
0 |
3,84 |
– |
101 |
Trial on wheat var. Yubileynaya 100.
Presowing treatment with full dose of fungicide – tebuconazole 0.5 L/tonne;
with reduced dose of fungicide - tebuconazole 0.35 L/tonne + Albit 40
ml/tonne. |
Ulyanovets LLC, 2005 |
| 13. |
propiconazole |
0.5 L/hectare |
0,35 L/hectare |
40 ml/hectare |
winter wheat |
– |
– |
– |
56 |
65.8 |
0 |
94,08 |
– |
118 |
Trial on wheat var. Lira. Presowing
treatment with full dose of fungicide – tebuconazole 0.5 L/tonne; with reduced
dose of fungicide -tebuconazole 0.35 L/tonne + Albit 40 ml/tonne. |
Ulyanovets LLC, 2005 |
| 14. |
propiconazole |
0.5 L/hectare |
0,35 L/hectare |
40 ml/hectare |
winter wheat |
– |
– |
– |
43 |
49 |
0 |
57,6 |
– |
114 |
Trial on wheat var. Deya. Presowing
treatment with full dose of fungicide – tebuconazole 0.5 L/tonne; with reduced
dose of fungicide -tebuconazole 0.35 L/tonne + Albit 40 ml/tonne. |
Ulyanovets LLC, 2005 |
| 15. |
triadimefon |
0.2 êã / ãà |
0,1 êã / ãà |
200 ml/hectare |
vine |
downy mildew |
41 |
51 |
83 |
86 |
- |
- |
124 |
– |
Yeld was characterised as percent of ripened
berries. The average annual shoot increment in triadimefon variant
is 334 cm; in variant treated with Albit/Baileton combination - 424 cm. |
All-Russia Institute of Viticulture and
Vine Processing, 2003 |
| 16. |
triadimefon |
0.2 êã/ãà |
0,1 êã/ãà |
200 ml/hectare |
vine |
powdery
mildew |
31/39 |
37/45 |
83 |
86 |
- |
- |
117 |
– |
Yeld was characterised as percent of ripened
berries. BE was calculated in accordance to scheme ‘leaves/shoots’. The
average annual shoot increment in triadimefon variant is 334 cm;
in variant treated with Albit/Baileton combination - 424 cm. |
All-Russia Institute of Viticulture and
Vine Processing, 2003 |
| 17. |
benomyl |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
winter wheat |
Septoria leaf
spot |
50 |
46 |
47.6 |
47.6 |
- |
- |
92 |
100 |
Var. Pobeda. The maximal infestation
of plants was considered as 5 points. BE was calculated basing on infestation
points in concrete variants. |
Bio-Rost LLC, 2005 |
| 18. |
benomyl |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
winter wheat |
Septoria leaf
spot |
60 |
66 |
50.2 |
51.3 |
- |
- |
110 |
102 |
Var. Pobeda. Double foliar spraying
with Albit, 40 ml/hectare. The maximal infestation of plants was considered
as 5 points. BE was calculated basing on infestation points in concrete
variants. |
Bio-Rost LLC, 2005 |
| 19. |
benomyl |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
winter wheat |
Septoria leaf
spot |
46 |
56 |
45.8 |
47.8 |
- |
- |
122 |
104 |
Var. Don 95. The maximal infestation
of plants was considered as 5 points. BE was calculated basing on infestation
points in concrete variants. |
Bio-Rost LLC, 2005 |
| 20. |
benomyl |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
winter wheat |
Septoria leaf
spot |
60 |
64 |
48.7 |
48.6 |
- |
- |
107 |
100 |
Var. Don 95. Double foliar spraying
with Albit, 40 ml/hectare. The maximal infestation of plants was considered
as 5 points. BE was calculated basing on infestation points in concrete
variants |
Bio-Rost LLC, 2005 |
| 21. |
benomyl |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
winter wheat |
Septoria leaf
spot |
60 |
56 |
54.5 |
54.8 |
- |
- |
93 |
101 |
Var. Prikumskaya 140. The maximal
infestation of plants was considered as 5 points. BE was calculated basing
on infestation points in concrete variants |
Bio-Rost LLC, 2005 |
| 22. |
benomyl |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
winter wheat |
Septoria leaf
spot |
60 |
80 |
58 |
57.7 |
- |
- |
133 |
99 |
Var. Prikumskaya 140. Double
foliar spraying with Albit, 40 ml/hectare. The maximal infestation of
plants was considered as 5 points. BE was calculated basing on infestation
points in concrete variants |
Bio-Rost LLC, 2005 |
| 23. |
benomyl |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
winter wheat |
Septoria leaf
spot |
74 |
80 |
47.2 |
50.2 |
- |
- |
108 |
106 |
Var. Prikumskaya 124. The maximal
infestation of plants was considered as 5 points. BE was calculated basing
on infestation points in concrete variants |
Bio-Rost LLC, 2005 |
| 24. |
benomyl |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
winter wheat |
Septoria leaf
spot |
76 |
90 |
52.4 |
54.6 |
- |
- |
118 |
104 |
Var. Prikumskaya 124. Double
foliar spraying with Albit, 40 ml/hectare. The maximal infestation of
plants was considered as 5 points. BE was calculated basing on infestation
points in concrete variants |
Bio-Rost LLC, 2005 |
| 25. |
benomyl |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
winter wheat |
Septoria leaf
spot |
60 |
70 |
52.6 |
53 |
- |
- |
117 |
101 |
Var. Prikumskaya 152. The maximal
infestation of plants was considered as 5 points. BE was calculated basing
on infestation points in concrete variants |
Bio-Rost LLC, 2005 |
| 26. |
benomyl |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
winter wheat |
Septoria leaf
spot |
80 |
84 |
57 |
58.4 |
- |
- |
105 |
102 |
Var. Prikumskaya 152. Double
foliar spraying with Albit, 40 ml/hectare. The maximal infestation of
plants was considered as 5 points. BE was calculated basing on infestation
points in concrete variants |
Bio-Rost LLC, 2005 |
| 27. |
thiabendazole + tebuconazole |
0.4 L/tonne |
0,2 L/tonne |
200 g/tonne |
sunflower |
watery soft rot |
57 |
63 |
24 |
24.5 |
63,48 |
74,48 |
111 |
102 |
The maximal effectiveness is in variant
with additional foliar spraying with Albit. Addition of Albit to thiabendazole/tebuconazole-based
fungicide increased germination by 2-15%, weight of 1000 seeds, diameter
of head. Yield in control was 21.0 centners/hectare. |
Agricultural Scientific Institute of South-East,
2003 |
| 28. |
thiabendazole + tebuconazole |
0.4 L/tonne |
0,2 L/tonne |
200 g/tonne |
sunflower |
head gray
mould blight |
67 |
71 |
24 |
24.5 |
63,48 |
74,48 |
106 |
102 |
The maximal effectiveness is in variant
with additional foliar spraying with Albit. Addition of Albit to thiabendazole/tebuconazole-based
fungicide increased germination by 2-15%, weight of 1000 seeds, diameter
of head. Yield in control was 21.0 centners/hectare. |
Agricultural Scientific Institute of South-East,
2003 |
| 29. |
thiabendazole + tebuconazole |
0.4 L/tonne |
0,2 L/tonne |
30 g/tonne |
winter wheat |
brown rust |
6 |
38 |
39.6 |
42 |
18 |
51,96 |
633 |
106 |
The average data of 3-years trials. Profitability
of thiabendazole/tebuconazole-based fungicide treatments is 150%; profitability
of treatment with combination of Albit + 1/2 dose of thiabendazole/tebuconazole-based
fungicide is 760%. Yield in control was 37.1 centners/hectare. |
Soil Institute and Kursk Regional Plant
Protection Station 2001-2003 |
| 30. |
thiabendazole + tebuconazole |
0.4 L/tonne |
0,2 L/tonne |
30 g/tonne |
winter wheat |
powdery
mildew |
5 |
24 |
39.6 |
42 |
18 |
51,96 |
480 |
106 |
The average data of 3-years trials. Profitability
of thiabendazole/tebuconazole-based fungicide treatments is 150%; profitability
of treatment with combination of Albit + 1/2 dose of Thiabendazole/tebuconazole-based
fungicide is 760%. Yield in control was 37.1 centners/hectare. |
Soil Institute and Kursk Regional Plant
Protection Station 2001-2003 |
| 31. |
thiabendazole + tebuconazole |
0.4 L/tonne |
0,2 L/tonne |
30 g/tonne |
winter wheat |
Septoria leaf
spot |
1 |
26 |
39.6 |
42 |
18 |
51,96 |
2600 |
106 |
The average data of 3-years trials. Profitability
of thiabendazole/tebuconazole-based fungicide treatments is 150%; profitability
of treatment with combination of Albit + 1/2 dose of Thiabendazole/tebuconazole-based
fungicide is 760%. Yield in control was 37.1 centners/hectare. |
Soil Institute and Kursk Regional Plant
Protection Station 2001-2003 |
| 32. |
thiabendazole + flutriafol |
– |
1 L/tonne |
40 g/tonne |
winter wheat |
root rots |
– |
100 |
– |
– |
- |
- |
– |
– |
Average yield was 45-49 centners/hectare
with glutent content of 23-29%. The Index of Gluten Deformation is 65-95.
Treatments provided improved winter survival and drought resistance.
Cost of treatment (comparing to treatment with pure pesticide) decreased
approx. twofold. |
Ecologiya LLC, 1999-2002 |
| 33. |
thiabendazole + flutriafol |
– |
1 L/tonne |
40 g/tonne |
winter wheat |
root rots |
– |
100 |
– |
19 |
- |
- |
– |
– |
Treatments provided visible improvement
of winter survival and drought resistance, 2-4 fold increase of rootage
weight. Column ‘yield’ contains percent of yield increase over control. |
Ecologiya LLC, 2001-2002 |
| 34. |
thiabendazole + flutriafol |
2 L/tonne |
0,30 L/tonne |
50 ml/tonne |
spring barley |
root rots |
100 |
100 |
21.9 |
24.1 |
- |
- |
100 |
110 |
Flutriafol with Albit were used for presowing
seed treatment as a part of combination ‘Albit-3’ (70 ml/tonne). Plants
treated with this combination reached EC stage 50-59 while plants in
control was in EC stage 29-39, i.e. forestalling in development was about
15 days. Yield in control was 18.7 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Institute of Leguminous and
Groat Crops, 2005 |
| 35. |
thiabendazole + flutriafol |
2 L/tonne |
0,30 L/tonne |
50 ml/tonne |
spring barley |
root rots |
100 |
100 |
56.5 |
59.4 |
- |
- |
100 |
105 |
Flutriafol with Albit were used for presowing
seed treatment as a part of combination ‘Albit-3’ (70 ml/tonne). Yield
in control was 50.3 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Institute of Leguminous and
Groat Crops, 2006 |
| 36. |
carboxin + thiram |
3 L/tonne |
1,5 ëò |
30 ml/tonne |
spring wheat |
root rots |
72 |
69 |
18.8 |
20.7 |
26,68 |
55,64 |
96 |
110 |
BE was calculated in EC stage 20-29. Yield
in control was 16.5 centners/hectare. |
Agricultural Scientific Institute of South-East,
2004 |
| 37. |
carboxin + thiram |
3 L/tonne |
1,5 ëò |
30 ml/tonne |
spring wheat |
root rots |
73 |
70 |
18.8 |
20.7 |
26,68 |
55,64 |
96 |
110 |
BE was calculated in EC stage 50-59. Yield
in control was 16.5 centners/hectare. |
Agricultural Scientific Institute of South-East,
2004 |
| 38. |
carboxin + thiram |
3 L/tonne |
1,5 ëò |
30 ml/tonne |
spring wheat |
loose smut |
100 |
100 |
18.8 |
20.7 |
26,68 |
55,64 |
100 |
110 |
Yield in control was 16.5 centners/hectare. |
Agricultural Scientific Institute of South-East,
2004 |
| 39. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 L/tonne |
1 L/tonne |
40 ml/tonne |
spring barley |
root rots |
44 |
100 |
– |
– |
- |
- |
227 |
– |
BE of trial with halved dose of fungicide
was considered as 100% (disease prevalence was 4%). Cost of treatment
of 1 tonne of grain in variant wariant with decreased fungicide rate
was decreased by 13.2 USD. |
Kurkino collective farm, 2002 |
| 40. |
thiram + tebuconazole ) |
1.5 L/tonne |
1 L/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
anthracnose |
96 |
96 |
46 |
49 |
- |
- |
100 |
107 |
Yield in control was 32.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2003 |
| 41. |
thiram + tebuconazole |
1.5 L/tonne |
1 L/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
anthracnose |
96 |
96 |
54 |
56 |
- |
- |
100 |
104 |
Additional treatment: Albit 50 g/hectare
+ herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-tefuryl. Yield in
control was 48.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2003 |
| 42. |
thiram + tebuconazole |
1.5 L/tonne |
1 L/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
anthracnose |
96 |
96 |
47 |
51 |
- |
- |
100 |
109 |
Additional treatment: Albit 50 g/hectare
+ herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-tefuryl. Yield in
control was 43.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2003 |
| 43. |
thiram + tebuconazole |
1.5 L/tonne |
1L/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
bacteriosis |
44 |
96 |
46 |
49 |
- |
- |
218 |
107 |
Yield in control was 32.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2003 |
| 44. |
thiram + tebuconazole |
1.5 L/tonne |
1L/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
bacteriosis |
44 |
96 |
54 |
56 |
- |
- |
218 |
104 |
Additional treatment: Albit 50 g/hectare
+ herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-tefuryl. Yield in
control was 48.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2003 |
| 45. |
thiram + tebuconazole |
1.5 L/tonne |
1L/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
bacteriosis |
44 |
96 |
47 |
51 |
- |
- |
218 |
109 |
Additional treatment: Albit 50 g/hectare
+ herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-tefuryl. Yield in
control was 43.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2003 |
| 46. |
thiram + tebuconazole |
1.5 L/tonne |
1 L/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
ozoniosis |
88 |
94 |
46 |
49 |
- |
- |
107 |
107 |
Yield in control was 32.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2003 |
| 47. |
thiram + tebuconazole |
1.5 L/tonne |
1 L/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
ozoniosis |
88 |
94 |
54 |
56 |
- |
- |
107 |
104 |
Additional treatment: Albit 50 g/hectare
+ herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-tefuryl. Yield in
control was 48.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2003 |
| 48. |
thiram + tebuconazole |
1.5 L/tonne |
1 L/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
ozoniosis |
88 |
94 |
47 |
51 |
- |
- |
107 |
109 |
Additional treatment: Albit 50 g/hectare
+ herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-tefuryl. Yield in
control was 43.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2003 |
| 49. |
thiram + tebuconazole |
2 L/tonne |
1 L/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
pasmo
disease |
8 |
14 |
46 |
49 |
- |
- |
175 |
107 |
Yield in control was 32.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2003 |
| 50. |
thiram + tebuconazole |
2 L/tonne |
1 L/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
pasmo
disease |
86 |
87 |
54 |
56 |
- |
- |
101 |
104 |
Additional treatment: Albit 50 g/hectare
+ herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-tefuryl. Yield in
control was 48.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2003 |
| 51. |
thiram + tebuconazole |
2 L/tonne |
1 L/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
pasmo
disease |
27 |
30 |
47 |
51 |
- |
- |
111 |
109 |
Additional treatment: Albit 50 g/hectare
+ herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-tefuryl. Yield in
control was 43.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2003 |
| 52. |
difenoconazole + cyproconazole |
1.0 L/tonne |
0,5 L/tonne |
40 ml/tonne |
winter wheat |
root rots |
66 |
67 |
85.9 |
85.4 |
- |
- |
102 |
99 |
Treatment with difenoconazole + cyproconazole sonsiderably
retarded germination under field conditions: by 10th day there was only
10% of germinated seeds (in untreated control – 50%), while treatment
with Albit provided 60%. Combined using of difenoconazole + cyproconazole and Albit provided
30% of germinated seeds by this time. |
All-Russia Institute of Plant Protection,
2004-2005 |
| 53. |
difenoconazole + cyproconazole |
1.0 L/tonne |
0,5 L/tonne |
40 ml/tonne |
winter wheat |
stinking smut |
100 |
100 |
85.9 |
85.4 |
- |
- |
100 |
99 |
|
All-Russia Institute of Plant Protection,
2004-2005 |
| 54. |
difenoconazole + cyproconazole |
1 L/tonne |
0,7 L/tonne |
40 ml/tonne |
winter wheat |
– |
– |
– |
57 |
64.7 |
- |
- |
– |
114 |
Var. Krasnodarskaya 99. Foliar
treatment with full rate of flurtiafol-based fungicide –0.5 L/hectare,
decreased rate - 0.35 L/hectare + Albit 40 ml/hectare. |
Esentuki-khleb OSC, 2005 |
| 55. |
difenoconazole + cyproconazole |
1 L/tonne |
0,7 L/tonne |
40 ml/tonne |
winter wheat |
– |
– |
– |
45.2 |
49.5 |
- |
- |
– |
110 |
Var. Rufa. Foliar treatment with
full rate of flurtiafol-based fungicide –0.5 L/hectare, decreased rate
- 0.35 L/hectare + Albit 40 ml/hectare. |
Esentuki-khleb OSC, 2005 |
| 56. |
difenoconazole + cyproconazole |
1.5 L/tonne |
0,7 L/tonne |
40 ml/tonne |
spring barley |
Rhynchosporium leaf spot
|
0 |
90 |
45.1 |
56.4 |
- |
- |
– |
125 |
Efficiency was calculated regarding to
variant treated with full rate of difenoconazole/cyproconazole–based
fungicide (considered as 0) Tillering in variant with Albit treatment
is 1.7 shoots/plant, in control - 1.2. |
Vlad imir Regional Plant Protection Station,
2003 |
| 57. |
difenoconazole |
– |
1 L/tonne |
30 g/tonne |
spring wheat |
Helminthosporium rot |
– |
100 |
– |
21.7 |
- |
- |
– |
– |
Trial was carried out in anomalous cold
and wet 2001 (Kurgan oblast). Yield in control was 11.0 centners/hectare. |
Kurgan Regional Plant Protection Station,
2001 |
| 58. |
difenoconazole |
– |
1 L/tonne |
30 g/tonne |
spring wheat |
different seed moulds |
– |
100 |
– |
21.7 |
- |
- |
– |
– |
Trial was carried out in anomalous cold
and wet 2001 (Kurgan oblast).Yield in control was 11.0 centners/hectare. |
Kurgan Regional Plant Protection Station,
2001 |
| 59. |
difenoconazole |
– |
1 L/tonne |
30 g/tonne |
spring wheat |
Fuzarium head blight |
– |
100 |
– |
21.7 |
- |
- |
– |
– |
Trial was carried out in anomalous cold
and wet 2001 (Kurgan oblast).Yield in control was 11.0 centners/hectare. |
Kurgan Regional Plant Protection Station,
2001 |
| 60. |
flutriafol |
0.5 L/hectare |
0,35 L/hectare |
40 ml/hectare |
winter wheat |
– |
– |
– |
57 |
64.7 |
- |
- |
– |
114 |
Var. Krasnodarskaya 99. Presowing
seed treatment with full rate of difenoconazole/cyproconazole–based fungicide
- 1 L/tonne; with decreased rate - 0.5 L/tonne + Albit 40 ml/tonne. |
Esentuki-khleb OSC, 2005 |
| 61. |
flutriafol |
0.5 L/hectare |
0,35 L/hectare |
40 ml/hectare |
winter wheat |
– |
– |
– |
45.2 |
49.5 |
- |
- |
– |
110 |
Var. Rufa. Presowing seed treatment
with full rate of difenoconazole/cyproconazole–based fungicide - 1 L/tonne;
with decreased rate - 0.5 L/tonne + Albit 40 ml/tonne. |
Esentuki-khleb OSC, 2005 |
| 62. |
carbendazim + carboxin |
2.5 L/tonne |
1,25 L/tonne |
30 ml/hectare |
spring wheat |
loose smut |
85 |
80 |
21.5 |
23 |
42,04 |
62,56 |
94 |
107 |
Combination with Albit and carbendazim-based
fungicide increased germination and germination power (by 3-7%), ear
lenght (from 6.6 to 8.2 cm), weight of 1000 seeds (from 27.5 to 29 g)
as compared to treatment with pure fungicide. Yield in control was 17.5
centners/hectare. |
Agricultural Scientific Institute of South-East,
2002 |
| 63. |
carbendazim |
– |
1 L/tonne |
40 g/tonne |
winter wheat |
root rots |
– |
100 |
– |
– |
- |
- |
– |
– |
Average yield was 45-49 centners/hectare
with gluten content of 23-29% and Index of Gluten Deformation of 65-95.
Improved winter survival of plants and drought resistance. Cost of treatment
(comparing to that of full rate of fungicide) decreased approx. two-fold. |
Ecologiya LLC, 1999-2002 |
| 64. |
carbendazim + carboxin |
2.5 L/tonne |
1,25 L/tonne |
30 ml/hectare |
spring wheat |
root rots |
50 |
43 |
21.5 |
23 |
42,04 |
62,56 |
86 |
107 |
Combination of Albit and carbendazim-based
fungicide increased germination, germination power (by 3-7%), ear lenght
(from 6.6 to 8.2 cm), weight of 1000 grains (from 27.5 to 29 g) as compared
to treatment with pure fungicide. Yield in control was 17.5 centners/hectare. |
Agricultural Scientific Institute of South-East,
2002 |
| 65. |
mancozeb + metalaxyl + spiroxamine + tebuconazole
+ triadimenol + sulphur |
– |
– |
250 ã/ãà |
vine |
downy mildew |
92 |
99 |
128 |
132 |
- |
- |
108 |
– |
Trial was carried out in Yubileynoe collective
farm on var. Risling. Efficiency was calculated at 15th day
after treatment basing on increase of bunch weight over control. |
North-Caucasian Institute of Horticulture
and Viticulture, 2004 |
| 66. |
mancozeb + metalaxyl + spiroxamine + tebuconazole
+ triadimenol + sulphur |
– |
– |
250 ã/ãà |
vine |
powdery
mildew |
85 |
95 |
128 |
132 |
- |
- |
112 |
– |
Trial was carried out in Yubileynoe collective
farm on var. Risling. Data on disease prevalence and development
were taken at 20 Jul and 13 Aug. Yield was calculated basing on increase
of bunch weight over control. |
North-Caucasian Institute of Horticulture
and Viticulture, 2004 |
| 67. |
CuCl 2*3CuO 4H 2O + cymoxanil |
– |
1 êã/ãà |
40 ml/hectare |
potato |
late blight |
100 |
100 |
250 |
350 |
- |
- |
100 |
140 |
In combination with Albit, halved doses
of Cu/oxadixyl-based fungicide used insted of Cu/cymoxanil-based fungicide
provided analogous results. The analogous results of trials with Albit
were obtained in preceeding 2002 and 2003. Comparing to application of
full rate of the fungicide, the reduction of treatment expenses was 100-200
USD. |
Odoyevskie zori collective farm, 2004 |
| 68. |
tebuconazole |
0.5 L/tonne |
0,25 L/tonne |
30 ml/tonne |
spring barley |
root rots |
72 |
68 |
26 |
25.7 |
3,48 |
6,6 |
94 |
99 |
Instead of net profit from 1 hectare, the
profitability (%) was used. In case of application of full rate of tebuconazole-based
fungicide, the profitability was 90%, application of halved dose of the
fungicide + Albit provided 150% of profitability. Yield increase in variant
with halved dose of the fungicide (without Albit) was 9.5%, efficiency
against root rots - 56.6%. Yield in control was 22.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Institute of Plant Protection,
2004 |
| 69. |
tebuconazole |
0.5 L/tonne |
0,25 L/tonne |
30 ml/tonne |
spring barley |
loose smut |
79 |
64 |
26 |
25.7 |
3,48 |
6,6 |
81 |
99 |
Instead of net profit from 1 hectare, the
profitability (%) was used. In case of application of full rate of tebuconazole-based
fungicide, the profitability was 90%, application of halved dose of the
fungicide + Albit provided 150% of profitability. Yield increase in variant
with halved dose of the fungicide (without Albit) was 9.5%, efficiency
against root rots - 56.6%. Yield in control was 22.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Institute of Plant Protection,
2004 |
| 70. |
tebuconazole |
0.5 L/tonne |
0,25 L/tonne |
30 ml/tonne |
spring barley |
stinking smut |
93 |
75 |
26 |
25.7 |
3,48 |
6,6 |
81 |
99 |
Instead of net profit from 1 hectare, the
profitability (%) was used. In case of application of full rate of tebuconazole-based
fungicide, the profitability was 90%, application of halved dose of the
fungicide + Albit provided 150% of profitability. Yield increase in variant
with halved dose of the fungicide (without Albit) was 9.5%, efficiency
against root rots - 56.6%. Yield in control was 22.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Institute of Plant Protection,
2004 |
| 71. |
tebuconazole |
1.5 êg/tonne |
0,75 êg/tonne |
30 g/tonne |
spring wheat |
brown rust |
38 |
52 |
38.3 |
39.9 |
10,64 |
17,2 |
137 |
104 |
Yield in control was 34.3 centners/hectare. |
Soil Institute and Kursk Regional Plant
Protection Station 2002 |
| 72. |
tebuconazole |
1.5 êg/tonne |
0,75 êg/tonne |
30 ml/tonne |
spring barley |
brown rust |
17 |
37 |
38.9 |
39.7 |
1,84 |
5,2 |
218 |
102 |
Yield in control was 37.1 centners/hectare. |
Soil Institute and Kursk Regional Plant
Protection Station 2002 |
| 73. |
tebuconazole |
1.5 êg/tonne |
0,75 êg/tonne |
30 g/tonne |
spring wheat |
Septoria leaf
spot |
35 |
46 |
38.3 |
39.9 |
10,64 |
17,2 |
131 |
104 |
Yield in control was 34.3 centners/hectare. |
Soil Institute and Kursk Regional Plant
Protection Station 2002 |
| 74. |
tebuconazole |
0.75 êg/tonne |
1,5 êg/tonne |
30 ml/tonne |
spring barley |
Septoria leaf
spot |
22 |
43 |
38.9 |
39.7 |
1,84 |
5,2 |
195 |
102 |
Yield in control was 37.1 centners/hectare. |
Soil Institute and Kursk Regional Plant
Protection Station 2002 |
| 75. |
tebuconazole |
– |
0,7 êg/tonne |
30 g/tonne |
winter wheat |
stinking smut |
– |
100 |
– |
– |
- |
- |
– |
– |
Trial was carried out in Progress collective
farm. |
Saratov Regional Plant Protection Station,
2001 |
| 76. |
epoxiconazole |
0.8 L/hectare |
0,4 L/hectare |
40 ml/hectare |
winter wheat |
brown rust and other rusts |
87 |
84 |
54.1 |
54.8 |
- |
- |
97 |
101 |
Efficiency of halved dose of epoxiconazole-based
fubgicide (without Albit)was 45-56%, yield increase – 9%. Yield in control
was 45.4 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Institute of Biological Plant
Protection, 2004 |
| 77. |
epoxiconazole |
0.8 L/hectare |
0,4 L/hectare |
40 ml/hectare |
winter wheat |
Septoria leaf
spot and other
leaf spots |
76 |
76 |
54.1 |
54.8 |
- |
- |
100 |
101 |
Efficiency of halved dose of epoxiconazole-based
fubgicide (without Albit)was 45-56%, yield increase – 9%. Yield in control
was 45.4 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Institute of Biological Plant
Protection, 2004 |
| 78. |
mancozeb + mefenoxam + spiroxamine + tebuconazole
+ triadimenol + CuCl 2*3CuO 4H 2O + sulphur + flutriafol |
– |
– |
250 ã/ãà |
vine |
downy mildew |
93 |
91 |
125 |
135 |
- |
- |
98 |
– |
Trial was carried out in Golubaya bukhta
collective farm on vine var. Chardonnay . Data on disease prevalence
and development were taken at 20 Jul and 11 Aug. Treatment with chemical
standard provided plumpness of a bunch of 4.4 points, whereas treatment
with chemical standard/Albit combination – 4.8 points. Yield was calculated
basing on weight of bunch (in untreated control – 100%). |
North-Caucasian Institute of Horticulture
and Viticulture, 2004 |
| 79. |
mancozeb + mefenoxam + spiroxamine + tebuconazole
+ triadimenol + CuCl 2*3CuO 4H 2O + sulphur + flutriafol |
– |
– |
250 ã/ãà |
vine |
powdery mildew |
100 |
100 |
125 |
135 |
- |
- |
100 |
– |
Trial was carried out in Golubaya bukhta
collective farm on vine var. Chardonnay . Data on disease prevalence
and development were taken at 20 Jul and 11 Aug. Treatment with chemical
standard provided plumpness of a bunch of 4.4 points, whereas treatment
with chemical standard/Albit combination – 4.8 points. Yield was calculated
basing on weight of bunch (in untreated control – 100%). |
North-Caucasian Institute of Horticulture
and Viticulture, 2004 |
| 80. |
difenoconazole |
0.75 ìë/äå-ðåâî |
55 ìë/äå-ðåâî |
5 ìë/äå-ðåâî |
apple |
scab |
79/93 |
75/87 |
– |
– |
- |
- |
94 |
– |
Full dose of difenoconazole-based fungicide
provided photosinthetic leaf activity (Fv/Fm) of 0.73 units, whereas
its combination with Albit provided 0.75 units. Also, combination with
Albit provided 8% increased catalase activity, that characterise ability
of apple to resist diseases. BE calculated in accordance with scheme
‘leaves/fruits’. |
Michurin All-Russia Institute of Horticulture,
2002 |
| 81. |
tebuconazole |
0.5 L/tonne |
0,35 L/tonne |
40 ml/tonne |
winter wheat |
– |
– |
– |
53 |
58.8 |
0 |
55,68 |
– |
111 |
Var. Ermak. Foliar spraying with
full rate of propiconazole-based fungicide - 0.5 L/hectare, with decreased
- 0.35 L/hectare + Albit 40 ml/hectare. |
Ulyanovets LLC, 2005 |
| 82. |
tebuconazole |
0.5 L/tonne |
0,35 L/tonne |
40 ml/tonne |
winter wheat |
– |
– |
– |
52.8 |
53.2 |
0 |
3,84 |
– |
101 |
Var. Yubileynaya 100. Foliar
spraying with full rate of propiconazole-based fungicide - 0.5 L/hectare,
with decreased - 0.35 L/hectare + Albit 40 ml/hectare. |
Ulyanovets LLC, 2005 |
| 83. |
tebuconazole |
0.5 L/tonne |
0,35 L/tonne |
40 ml/tonne |
winter wheat |
– |
– |
– |
5 6 |
65.8 |
0 |
94,08 |
– |
118 |
Var. Lira. Foliar spraying with
full rate of propiconazole-based fungicide - 0.5 L/hectare, with decreased
- 0.35 L/hectare + Albit 40 ml/hectare. |
Ulyanovets LLC, 2005 |
| 84. |
tebuconazole |
0.5 L/tonne |
0,35 L/tonne |
40 ml/tonne |
winter wheat |
– |
– |
– |
43 |
49 |
0 |
57,6 |
– |
114 |
Var. Deya. Foliar spraying with
full rate of propiconazole-based fungicide - 0.5 L/hectare, with decreased
- 0.35 L/hectare + Albit 40 ml/hectare. |
Ulyanovets LLC, 2005 |
| 85. |
thiram |
4 êg/tonne |
2 êg/tonne |
50 ml/tonne |
pea |
root rots |
39 |
35 |
20.5 |
20.7 |
- |
- |
90 |
101 |
BE was determined in budding stage. Yield
in control was 16.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Institute of Leguminous and
Groat Crops, 2004 |
| 86. |
thiram |
4 êg/tonne |
2 êg/tonne |
50 ml/tonne |
pea |
root rots |
23 |
25 |
20.5 |
20.7 |
- |
- |
109 |
101 |
BE was determined in bean setting satage.
Yield in control was 16.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Institute of Leguminous and
Groat Crops, 2004 |
| 87. |
thiram |
4 êg/tonne |
2 êg/tonne |
50 ml/tonne |
pea |
root rots |
60 |
60 |
20.5 |
20.1 |
- |
- |
100 |
98 |
BE was determined in budding stage. Yield
in control was 17.2 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Institute of Leguminous and
Groat Crops, 2005 |
| 88. |
thiram |
4 êg/tonne |
2 êg/tonne |
50 ml/tonne |
pea |
root rots |
60 |
60 |
20.5 |
20.1 |
- |
- |
100 |
98 |
BE was determined in bean setting satage.
Yield in control was 17.2 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Institute of Leguminous and
Groat Crops, 2005 |
| 89. |
thiram |
4 êg/tonne |
2 êg/tonne |
50 ml/tonne |
pea |
root rots |
100 |
100 |
29 |
30.3 |
- |
- |
100 |
104 |
BE was determined in budding satage. Yield
in control was 26.3 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Institute of Leguminous and
Groat Crops, 2006 |
| 90. |
thiram |
4 êg/tonne |
2 êg/tonne |
50 ml/tonne |
pea |
root rots |
30 |
30 |
29 |
30.3 |
- |
- |
100 |
104 |
BE was determined in bean setting satage.
Yield in control was 26.3 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Institute of Leguminous and
Groat Crops, 2006 |
| 91. |
thiram |
4.5 L/tonne |
2,2 L/tonne |
150 ml/tonne |
potato |
common scab |
70 |
79 |
230 |
234 |
- |
- |
113 |
102 |
Treatment variants with participation of
Albit provided earlier coming-up. In variant with decreased fungicide
rate, additional foliar spraying with Albit (40 g/hectare) was used.
Yield in control was 217 centners/hectare. |
Meristemnye kultury collective farm, 2003 |
| 92. |
thiram |
4.5 L/tonne |
2,2 L/tonne |
150 ml/tonne |
potato |
Rhyzoctonia disease |
63 |
65 |
230 |
234 |
- |
- |
103 |
102 |
Treatment variants with participation of
Albit provided earlier coming-up. In variant with decreased fungicide
rate, additional foliar spraying with Albit (40 g/hectare) was used.
Yield in control was 217 centners/hectare. |
Meristemnye kultury collective farm, 2003 |
| 93. |
thiram |
4.5 L/tonne |
3 L/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
anthracnose |
68 |
91 |
43 |
47 |
- |
- |
134 |
109 |
Yield in control was 32.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2003 |
| 94. |
thiram |
4.5 L/tonne |
3 L/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
anthracnose |
68 |
91 |
52 |
54 |
- |
- |
134 |
104 |
Additional treatment: Albit 50 g/hectare
+ herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-tefuryl. Yield in
control was 48.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2003 |
| 95. |
thiram |
4.5 L/tonne |
3 L/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
anthracnose |
68 |
91 |
45 |
47 |
- |
- |
13 4 |
104 |
Additional treatment: Albit 50 g/hectare
+ herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-tefuryl. Yield in
control was 43.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2003 |
| 96. |
thiram |
4.5 L/tonne |
3 L/tonne |
70 g/tonne |
flax |
anthracnose |
81 |
94 |
35 |
39 |
- |
- |
116 |
111 |
Yield in control was 31.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2004 |
| 97. |
thiram |
4.5 L/tonne |
3 L/tonne |
70 g/tonne |
flax |
anthracnose |
81 |
94 |
48 |
51 |
- |
- |
116 |
106 |
Additional treatment: Albit 50 g/hectare
+ herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-ethyl Yield in control
was 46.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2004 |
| 98. |
thiram |
4.5 L/tonne |
3 L/tonne |
70 g/tonne |
flax |
anthracnose |
81 |
94 |
45 |
48 |
- |
- |
116 |
107 |
Additional treatment: Albit 50 g/hectare
+ herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-ethyl. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2004 |
| 99. |
thiram |
4.5 êg/tonne |
3 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
anthracnose |
68 |
91 |
36 |
40 |
- |
- |
134 |
111 |
Germination: in control - 54%, in variant
with thiram-based fungicide – 56%, in variant with combination of the
fungicide and Albit – 61%. Yield in control was 33.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2005 |
| 100. |
thiram |
4.5 êg/tonne |
3 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
anthracnose |
68 |
91 |
47 |
50 |
- |
- |
134 |
106 |
Germination: in control - 54%, in variant
with thiram-based fungicide – 56%, in variant with combination of the
fungicide and Albit – 61%. Additional treatment: Albit 50 g/hectare +
herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-ethyl. Yield in control
was 44.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2005 |
| 101. |
thiram |
4.5 êg/tonne |
3 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
anthracnose |
68 |
91 |
45 |
48 |
- |
- |
134 |
107 |
Germination: in control - 54%, in variant
with thiram-based fungicide – 56%, in variant with combination of the
fungicide and Albit – 61%. Additional treatment: Albit 50 g/hectare +
herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-ethyl. Yield in control
was 42.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2005 |
| 102. |
thiram |
4.5 êg/tonne |
3 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
anthracnose |
60 |
80 |
38 |
44 |
- |
- |
133 |
116 |
Germination: in control - 51%, in variant
with thiram-based fungicide – 53%, in variant with combination of the
fungicide and Albit – 57%. Yield in control was 35.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2006 |
| 103. |
thiram |
4.5 êg/tonne |
3 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
anthracnose |
60 |
80 |
51 |
54 |
- |
- |
133 |
106 |
Germination: in control - 51%, in variant
with thiram-based fungicide – 53%, in variant with combination of the
fungicide and Albit – 57%. Additional treatment: Albit 50 g/hectare +
herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-ethyl. Yield in control
was 48.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2006 |
| 104. |
thiram |
4.5 êg/tonne |
3 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
anthracnose |
60 |
80 |
48 |
51 |
- |
- |
133 |
106 |
Germination: in control - 51%, in variant
with thiram-based fungicide – 53%, in variant with combination of the
fungicide and Albit – 57%. Additional treatment: Albit 50 g/hectare +
herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-ethyl. Yield in control
was 44.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2006 |
| 105. |
thiram |
4.5 L/tonne |
3 L/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
bacteriosis |
40 |
84 |
43 |
47 |
- |
- |
210 |
109 |
Yield in control was 32.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2003 |
| 106. |
thiram |
4.5 L/tonne |
3 L/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
bacteriosis |
40 |
84 |
52 |
54 |
- |
- |
210 |
104 |
Additional treatment: Albit 50 g/hectare
+ herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-tefuryl. Yield in
control was 48.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2003 |
| 107. |
thiram |
4.5 L/tonne |
3 L/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
bacteriosis |
40 |
84 |
45 |
47 |
- |
- |
210 |
104 |
Additional treatment: Albit 50 g/hectare
+ herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-tefuryl. Yield in
control was 43.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2003 |
| 108. |
thiram |
4.5 L/tonne |
3 L/tonne |
70 g/tonne |
flax |
bacteriosis |
50 |
96 |
35 |
39 |
- |
- |
192 |
111 |
Yield in control was 31.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2004 |
| 109. |
thiram |
4.5 L/tonne |
3 L/tonne |
70 g/tonne |
flax |
bacteriosis |
50 |
96 |
48 |
51 |
- |
- |
192 |
106 |
Additional treatment: Albit 50 g/hectare
+ herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-tefuryl. Yield in
control was 46.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2004 |
| 110. |
thiram |
4.5 L/tonne |
3 L/tonne |
70 g/tonne |
flax |
bacteriosis |
50 |
96 |
45 |
48 |
- |
- |
192 |
107 |
Additional treatment: Albit 50 g/hectare
+ herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-tefuryl. Yield in
control was 42.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2004 |
| 111. |
thiram |
4.5 êg/tonne |
3 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
bacteriosis |
38 |
88 |
36 |
40 |
- |
- |
232 |
111 |
Germination: in control - 54%, in variant
with thiram-based fungicide – 56%, in variant with combination of the
fungicide and Albit – 61%. Yield in control was 33.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2005 |
| 112. |
thiram |
4.5 êg/tonne |
3 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
bacteriosis |
38 |
88 |
47 |
50 |
- |
- |
232 |
106 |
Germination: in control - 54%, in variant
with thiram-based fungicide – 56%, in variant with combination of the
fungicide and Albit – 61%. Additional treatment: Albit 50 g/hectare +
herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-ethyl. Yield in control
was 44.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2005 |
| 113. |
thiram |
4.5 êg/tonne |
3 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
bacteriosis |
38 |
88 |
45 |
48 |
- |
- |
232 |
107 |
Germination: in control - 54%, in variant
with thiram-based fungicide – 56%, in variant with combination of the
fungicide and Albit – 61%. Additional treatment: Albit 50 g/hectare +
herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-ethyl. Yield in control
was 42.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2005 |
| 114. |
thiram |
4.5 êg/tonne |
3 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
bacteriosis |
24 |
69 |
38 |
44 |
- |
- |
288 |
116 |
Germination: in control - 51%, in variant
with thiram-based fungicide – 53%, in variant with combination of the
fungicide and Albit – 57%. Yield in control was 35.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2006 |
| 115. |
thiram |
4.5 êg/tonne |
3 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
bacteriosis |
24 |
69 |
51 |
54 |
- |
- |
288 |
106 |
Germination: in control - 51%, in variant
with thiram-based fungicide – 53%, in variant with combination of the
fungicide and Albit – 57%. Additional treatment: Albit 50 g/hectare +
herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-ethyl. Yield in control
was 48.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2006 |
| 116. |
thiram |
4.5 êg/tonne |
3 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
bacteriosis |
24 |
69 |
48 |
51 |
- |
- |
288 |
106 |
Germination: in control - 51%, in variant
with thiram-based fungicide – 53%, in variant with combination of the
fungicide and Albit – 57%. Additional treatment: Albit 50 g/hectare +
herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-ethyl. Yield in control
was 44.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2006 |
| 117. |
thiram |
4.5 L/tonne |
3 L/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
ozoniosis |
53 |
82 |
43 |
47 |
- |
- |
155 |
109 |
Yield in control was 32.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2003 |
| 118. |
thiram |
4.5 L/tonne |
3 L/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
ozoniosis |
53 |
82 |
52 |
54 |
- |
- |
155 |
104 |
Additional treatment: Albit 50 g/hectare
+ herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-tefuryl. Yield in
control was 48.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2003 |
| 119. |
thiram |
4.5 L/tonne |
3 L/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
ozoniosis |
53 |
82 |
45 |
47 |
- |
- |
155 |
104 |
Additional treatment: Albit 50 g/hectare
+ herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-tefuryl. Yield in
control was 43.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2003 |
| 120. |
thiram |
4.5 L/tonne |
3 L/tonne |
70 g/tonne |
flax |
ozoniosis |
79 |
92 |
35 |
39 |
- |
- |
116 |
111 |
Yield in control was 31.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2004 |
| 121. |
thiram |
4.5 L/tonne |
3 L/tonne |
70 g/tonne |
flax |
ozoniosis |
79 |
92 |
48 |
51 |
- |
- |
116 |
106 |
Additional treatment: Albit 50 g/hectare
+ herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-ethyl. Yield in
control was 46.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2004 |
| 122. |
thiram |
4.5 L/tonne |
3 L/tonne |
70 g/tonne |
flax |
ozoniosis |
79 |
92 |
45 |
48 |
- |
- |
116 |
107 |
Additional treatment: Albit 50 g/hectare
+ herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-ethyl. Yield in
control was 42.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2004 |
| 123. |
thiram |
4.5 êg/tonne |
3 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
ozoniosis |
66 |
84 |
36 |
40 |
- |
- |
127 |
111 |
Germination: in control - 54%, in variant
with thiram-based fungicide – 57%, in variant with combination of the
fungicide and Albit – 61%. Yield in control was 33.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2005 |
| 124. |
thiram |
4.5 ê g/tonne |
3 ê g/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
ozoniosis |
66 |
84 |
47 |
50 |
- |
- |
127 |
106 |
Germination: in control - 54%, in variant
with thiram-based fungicide – 57%, in variant with combination of the
fungicide and Albit – 61%. Additional treatment: Albit 50 g/hectare+
herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-ethyl. Yield in control
was 44.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2005 |
| 125. |
thiram |
4.5 êg/tonne |
3 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
ozoniosis |
66 |
84 |
45 |
48 |
- |
- |
127 |
107 |
Germination: in control - 54%, in variant
with thiram-based fungicide – 57%, in variant with combination of the
fungicide and Albit – 61%. Additional treatment: herbicides based on
chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-ethyl. Yield in control was 42.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2005 |
| 126. |
thiram |
4.5 êg/tonne |
3 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
ozoniosis |
54 |
63 |
38 |
44 |
- |
- |
117 |
116 |
Germination: in control - 51%, in variant
with thiram-based fungicide – 53%, in variant with combination of the
fungicide and Albit – 57%. Yield in control was 35.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2006 |
| 127. |
thiram |
4.5 êg/tonne |
3 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
ozoniosis |
54 |
63 |
51 |
54 |
- |
- |
117 |
106 |
Germination: in control - 51%, in variant
with thiram-based fungicide – 53%, in variant with combination of the
fungicide and Albit – 57%. Additional treatment: Albit 50 g/hectare +
herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-ethyl. Yield in control
was 48.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2006 |
| 128. |
thiram |
4.5 êg/tonne |
3 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
ozoniosis |
54 |
63 |
48 |
51 |
- |
- |
117 |
106 |
Germination: in control - 51%, in variant
with thiram-based fungicide – 53%, in variant with combination of the
fungicide and Albit – 57%. Additional treatment: herbicides based on
chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-ethyl. Yield in control was 44.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2006 |
| 129. |
thiram |
4.5 L/tonne |
3 L/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
pasmo disease |
5 |
10 |
43 |
47 |
- |
- |
200 |
109 |
Yield in control was 32.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2003 |
| 130. |
thiram |
4.5 L/tonne |
3 L/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
pasmo disease |
84 |
87 |
52 |
54 |
- |
- |
104 |
104 |
Additional treatment: Albit 50 g/hectare
+ herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-tefuryl. Yield in
control was 48.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2003 |
| 131. |
thiram |
4.5 L/tonne |
3 L/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
pasmo disease |
24 |
28 |
45 |
47 |
- |
- |
117 |
104 |
Additional treatment: Albit 50 g/hectare
+ herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-tefuryl. Yield in
control was 43.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2003 |
| 132. |
thiram |
4.5 L/tonne |
3 L/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
pasmo disease |
6 |
14 |
35 |
39 |
- |
- |
233 |
111 |
Yield in control was 31.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2004 |
| 133. |
thiram |
4.5 L/tonne |
3 L/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
pasmo disease |
78 |
83 |
48 |
51 |
- |
- |
106 |
106 |
Additional treatment: Albit 50 g/hectare
+ herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-ethyl. Yield in
control was 46.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2004 |
| 134. |
thiram |
4.5 L/tonne |
3 L/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
pasmo disease |
20 |
25 |
45 |
48 |
- |
- |
125 |
107 |
Additional treatment: Albit 50 g/hectare
+ herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-ethyl. Yield in
control was 42.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2004 |
| 135. |
thiram |
4.5 êg/tonne |
3 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
pasmo disease |
8 |
23 |
36 |
40 |
- |
- |
288 |
111 |
Germination: in control - 54%, in variant
with thiram-based fungicide – 57%, in variant with combination of the
fungicide and Albit – 61%.Yield in control was 33.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2005 |
| 136. |
thiram |
4.5 êg/tonne |
3 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
pasmo disease |
58 |
62 |
47 |
50 |
- |
- |
107 |
106 |
Germination: in control - 54%, in variant
with thiram-based fungicide – 57%, in variant with combination of the
fungicide and Albit – 61%.Additional treatment: Albit 50 g/hectare+ herbicides
based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-ethyl. Yield in control was 44.0
centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2005 |
| 137. |
thiram |
4.5 êg/tonne |
3 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
pasmo disease |
19 |
27 |
45 |
48 |
- |
- |
142 |
107 |
Germination: in control - 54%, in variant
with thiram-based fungicide – 57%, in variant with combination of the
fungicide and Albit – 61%. Additional treatment: herbicides based on
chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-ethyl. Yield in control was 42.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2005 |
| 138. |
thiram |
4.5 êg/tonne |
3 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
pasmo disease |
10 |
19 |
38 |
44 |
- |
- |
190 |
116 |
Germination: in control - 51%, in variant
with thiram-based fungicide – 53%, in variant with combination of the
fungicide and Albit – 57%. Yield in control was 35.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2006 |
| 139. |
thiram |
4.5 êg/tonne |
3 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
pasmo disease |
62 |
71 |
51 |
54 |
- |
- |
115 |
106 |
Germination: in control - 51%, in variant
with thiram-based fungicide – 53%, in variant with combination of the
fungicide and Albit – 57%. Additional treatment: Albit 50 g/hectare +
herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-ethyl. Yield in control
was 48.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2006 |
| 140. |
thiram |
4.5 êg/tonne |
3 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
pasmo disease |
33 |
43 |
48 |
51 |
- |
- |
130 |
106 |
Germination: in control - 51%, in variant
with thiram-based fungicide – 53%, in variant with combination of the
fungicide and Albit – 57%. Additional treatment: herbicides based on
chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-ethyl. Yield in control was 44.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2006 |
| 141. |
thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 ml/tonne |
ñîÿ |
Ascochyta leaf and pod spots |
67 |
67 |
16.1 |
17.4 |
- |
- |
100 |
108 |
Weight of 1000 beans and number of pods
are the largest in variant of treatment with thiram-based fungicide +
Albit. Yield in control was 14.1 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Institute of Plant Protection,
2004 |
| 142. |
thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
ñîÿ |
Septoria brown spot |
59 |
62 |
16.1 |
17.4 |
- |
- |
105 |
108 |
Weight of 1000 beans and number of pods
are the largest in variant of treatment with thiram-based fungicide +
Albit. Yield in control was 14.1 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Institute of Plant Protection,
2004 |
| 143. |
thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
ñîÿ |
Fusarium
seedling
root rot |
73 |
76 |
16.1 |
17.4 |
- |
- |
104 |
108 |
Weight of 1000 beans and number of pods
are the largest in variant of treatment with thiram-based fungicide +
Albit. Yield in control was 14.1 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Institute of Plant Protection,
2004 |
| 144. |
spiroxamine + tebuconazole + triadimenol |
0.6 L/hectare |
0,3 L/hectare |
40 ml/hectare |
winter wheat |
brown rust and other rusts |
91 |
89 |
54.4 |
54.3 |
- |
- |
98 |
100 |
Efficiency of the halved dose of spiroxamine/tebuconazole/triadimenol-based
fungicide was 48-60%, while yeld increase was 9.9% . Yield in control
was 45.4 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Institute of Biological Plant
Protection, 2004 |
| 145. |
spiroxamine + tebuconazole + triadimenol |
0.6 L/hectare |
0,3 L/hectare |
40 ml/hectare |
winter wheat |
Septoria leaf
spot and other
leaf spots |
81 |
80 |
54.4 |
54.3 |
- |
- |
99 |
100 |
Efficiency of the halved dose of spiroxamine/tebuconazole/triadimenol-based
fungicide was 48-60%, while yeld increase was 9.9%. Yield in control
was 45.4 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Institute of Biological Plant
Protection, 2004 |
| 146. |
spiroxamine + tebuconazole + triadimenol
+ flutriafol + karbendazim + sulphur |
- |
- |
250 ã/ãà |
vine |
powdery mildew |
97 |
90 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
93 |
- |
Savings on means of protection was 60 USD/hectare. |
North-Caucasian Institute of Horticulture
and Viticulture, 2006 |
| 147. |
spiroxamine + tebuconazole + triadimenol
+ flutriafol + karbendazim + sulphur |
- |
- |
250 ã/ãà |
vine |
white rot |
76 |
33 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
43 |
- |
Savings on means of protection was 60 USD/hectare. |
North-Caucasian Institute of Horticulture
and Viticulture, 2006 |
| 148. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
70 g/tonne |
flax |
anthracnose |
92 |
92 |
28 |
29 |
- |
- |
100 |
104 |
Yield in control was 22.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2002 |
| 149. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
70 g/tonne |
flax |
anthracnose |
92 |
92 |
30 |
31 |
- |
- |
100 |
103 |
Additional treatment: benomyl-based fungicide
+ herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-tefuryl. Yield in
control was 27.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2002 |
| 150. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
70 g/tonne |
flax |
anthracnose |
92 |
92 |
31 |
34 |
- |
- |
100 |
110 |
Additional treatment: Albit 50 g/hectare
+ herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-tefuryl. Yield in
control was 26.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2002 |
| 151. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
70 g/tonne |
flax |
anthracnose |
92 |
92 |
34 |
35 |
- |
- |
100 |
103 |
Additional treatment: Albit 50 g/hectare
+ benomyl-based fungicide + herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-tefuryl.
Yield in control was 29.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2002 |
| 152. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
70 g/tonne |
flax |
anthracnose |
92 |
92 |
28 |
29 |
- |
- |
100 |
104 |
Additional treatment: Albit 50 g/hectare.
Yield in control was 23.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2002 |
| 153. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
70 g/tonne |
flax |
anthracnose |
92 |
92 |
30 |
32 |
- |
- |
100 |
107 |
Additional treatment: Albit 50 g/hectare
+ herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-tefuryl. Yield in
control was 25.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2002 |
| 154. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
anthracnose |
95 |
95 |
41 |
45 |
- |
- |
100 |
110 |
Yield in control was 37.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2003 |
| 155. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
anthracnose |
95 |
95 |
47 |
49 |
- |
- |
100 |
104 |
Additional treatment: Benomyl-based fungicide
+ herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-tefuryl. Yield in
control was 45.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2003 |
| 156. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
anthracnose |
95 |
95 |
49 |
52 |
- |
- |
100 |
106 |
Additional treatment: Albit 50 g/hectare
+ herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-tefuryl. Yield in
control was 46.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2003 |
| 157. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
anthracnose |
95 |
95 |
45 |
47 |
- |
- |
100 |
104 |
Additional treatment: Albit 50 g/hectare
+ herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-tefuryl. Yield in
control was 40.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2003 |
| 158. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
anthracnose |
95 |
95 |
33 |
38 |
57 |
127,2 |
100 |
115 |
Combination of fungicide with Albit considerably
improved fibre quality: application of halved dose of carboxin/thiram
based fungicide with Albit provided increase of average number of fibre
by 11 units (comparing to application of pure fungicide). Increase of
percent-number of fibre: pure fungicide - 26%; Albit/fungicide – 65%.
Yield in control was 29.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2004 |
| 159. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
anthracnose |
95 |
95 |
41 |
44 |
72,2 |
126,4 |
100 |
107 |
Combination of fungicide with Albit considerably
improved fibre quality: application of halved dose of carboxin/thiram
based fungicide with Albit provided increase of average number of fibre
by 11 units (comparing to application of pure fungicide). Increase of
percent-number of fibre: pure fungicide - 26%; Albit/fungicide – 65%.
Additional treatment: benomyl-based fungicide + herbicides based on chlorsulfuron
and quizalofop-p-ethyl. Yield in control was 38.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2004 |
| 160. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
anthracnose |
95 |
95 |
43 |
48 |
78 |
154 |
100 |
112 |
Combination of fungicide with Albit considerably
improved fibre quality: application of halved dose of carboxin/thiram
based fungicide with Albit provided increase of average number of fibre
by 11 units (comparing to application of pure fungicide). Increase of
percent-number of fibre: pure fungicide - 26%; Albit/fungicide – 65%.
Additional treatment: benomyl-based fungicide + herbicides based on chlorsulfuron
and quizalofop-p-ethyl. Yield in control was 40.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2004 |
| 161. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
anthracnose |
95 |
95 |
39 |
42 |
70 |
124,2 |
100 |
108 |
Combination of fungicide with Albit considerably
improved fibre quality: application of halved dose of carboxin/thiram
based fungicide with Albit provided increase of average number of fibre
by 11 units (comparing to application of pure fungicide). Increase of
percent-number of fibre: pure fungicide - 26%; Albit/fungicide – 65%.
Additional treatment: benomyl-based fungicide + herbicides based on chlorsulfuron
and quizalofop-p-ethyl. Yield in control was 37.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2004 |
| 162. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
anthracnose |
92 |
96 |
31 |
35 |
- |
- |
104 |
113 |
Germination: in control - 53%, in variant
with carboxin/thiram -based fungicide – 56%, in variant with combination
of the fungicide and Albit – 60%. Yield in control was 25.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2005 |
| 163. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
anthracnose |
92 |
96 |
40 |
43 |
- |
- |
104 |
108 |
Germination: in control - 53%, in variant
with carboxin/thiram -based fungicide – 56%, in variant with combination
of the fungicide and Albit – 60%. Additional treatment: benomyl-based
fungicide + herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-ethyl.
Yield in control was 35.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2005 |
| 164. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
anthracnose |
92 |
96 |
42 |
46 |
- |
- |
104 |
110 |
Germination: in control - 53%, in variant
with carboxin/thiram -based fungicide – 56%, in variant with combination
of the fungicide and Albit – 60%. Additional treatment: Albit 50 g/hectare+
herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-ethyl. Yield in control
was 36.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2005 |
| 165. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
anthracnose |
92 |
96 |
37 |
41 |
- |
- |
104 |
111 |
Germination: in control - 53%, in variant
with carboxin/thiram -based fungicide – 56%, in variant with combination
of the fungicide and Albit – 60%. Additional treatment: herbicides based
on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-ethyl. Yield in control was 32.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2005 |
| 166. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 ml/tonne |
flax |
anthracnose |
82 |
86 |
30 |
33 |
- |
- |
105 |
110 |
Germination: in control - 48%, in variant
with carboxin/thiram/carboxin-based fungicide – 51%, in variant with
combination of the fungicide and Albit – 55%. Yield in control was 21.0
centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2006 |
| 167. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 ml/tonne |
flax |
anthracnose |
82 |
86 |
40 |
43 |
- |
- |
105 |
108 |
Germination: in control - 48%, in variant
with carboxin/thiram/carboxin-based fungicide – 51%, in variant with
combination of the fungicide and Albit – 55%. Additional treatment: benomyl
1 kg/hectare+ herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-ethyl.
Yield in control was 32.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2006 |
| 168. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 ml/tonne |
flax |
anthracnose |
82 |
86 |
42 |
45 |
- |
- |
105 |
107 |
Germination: in control - 48%, in variant
with carboxin/thiram/carboxin-based fungicide – 51%, in variant with
combination of the fungicide and Albit – 55%. Additional treatment: Albit
50 g/hectare + herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-ethyl.
Yield in control was 34.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2006 |
| 169. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 ml/tonne |
flax |
anthracnose |
82 |
86 |
34 |
40 |
- |
- |
105 |
118 |
Germination: in control - 48%, in variant
with carboxin/thiram/carboxin-based fungicide – 51%, in variant with
combination of the fungicide and Albit – 55%. Additional treatment: herbicides
based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-ethyl. Yield in control was 30.0
centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2006 |
| 170. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
70 g/tonne |
flax |
bacteriosis |
46 |
86 |
28 |
29 |
- |
- |
187 |
104 |
Yield in control was 22.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2002 |
| 171. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
70 g/tonne |
flax |
bacteriosis |
46 |
86 |
30 |
31 |
- |
- |
187 |
103 |
Additional treatment: benomyl-based fungicide
+ herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-tefuryl. Yield in
control was 27.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2002 |
| 172. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
70 g/tonne |
flax |
bacteriosis |
46 |
86 |
31 |
34 |
- |
- |
187 |
110 |
Additional treatment: Albit 50 g/hectare
+ herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-tefuryl. Yield in
control was 26.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2002 |
| 173. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
70 g/tonne |
flax |
bacteriosis |
46 |
86 |
34 |
35 |
- |
- |
187 |
103 |
Additional treatment: Albit 50 g/hectare+
benomyl-based fungicide + herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-tefuryl.
Yield in control was 29.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2002 |
| 174. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 ê g/tonne |
1 ê g/tonne |
70 g/tonne |
flax |
bacteriosis |
46 |
86 |
28 |
29 |
- |
- |
187 |
104 |
Additional treatment: Albit 50 g/hectare.
Yield in control was 23.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2002 |
| 175. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
70 g/tonne |
flax |
bacteriosis |
46 |
86 |
30 |
32 |
- |
- |
187 |
107 |
Additional treatment: Albit 50 g/hectare
+ herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-tefuryl. Yield in
control was 25.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2002 |
| 176. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
bacteriosis |
43 |
89 |
41 |
45 |
- |
- |
207 |
110 |
Yield in control was 37.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2003 |
| 177. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
bacteriosis |
43 |
89 |
47 |
49 |
- |
- |
207 |
104 |
Additional treatment: benomyl-based fungicide
+ herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-tefuryl. Yield in
control was 45.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2003 |
| 178. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
bacteriosis |
43 |
89 |
49 |
52 |
- |
- |
207 |
106 |
Additional treatment: Albit 50 g/hectare
+ herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-tefuryl. Yield in
control was 46.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2003 |
| 179. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
bacteriosis |
43 |
89 |
45 |
47 |
- |
- |
207 |
104 |
Additional treatment: Albit 50 g/hectare
+ herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-tefuryl. Yield in
control was 40.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2003 |
| 180. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
bacteriosis |
43 |
89 |
8 |
15 |
- |
- |
207 |
188 |
– |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2003 |
| 181. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
bacteriosis |
48 |
92 |
33 |
38 |
57 |
127,2 |
192 |
115 |
Combination of fungicide with Albit considerably
improved fibre quality: application of halved dose of carboxin/thiram
based fungicide with Albit provided increase of average number of fibre
by 11 units (comparing to application of pure fungicide). Increase of
percent-number of fibre: pure fungicide - 26%; Albit/fungicide – 65%.
Yield in control was 29.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2004 |
| 182. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
bacteriosis |
48 |
92 |
41 |
44 |
72,2 |
126,4 |
192 |
107 |
Combination of fungicide with Albit considerably
improved fibre quality: application of halved dose of carboxin/thiram
based fungicide with Albit provided increase of average number of fibre
by 11 units (comparing to application of pure fungicide). Increase of
percent-number of fibre: pure fungicide - 26%; Albit/fungicide – 65%.
Additional treatment: Benomyl-based fungicide + herbicides based on chlorsulfuron
and quizalofop-p-ethyl. Yield in control was 38.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2004 |
| 183. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
bacteriosis |
48 |
92 |
43 |
48 |
78 |
154 |
192 |
112 |
Combination of fungicide with Albit considerably
improved fibre quality: application of halved dose of carboxin/thiram
based fungicide with Albit provided increase of average number of fibre
by 11 units (comparing to application of pure fungicide). Increase of
percent-number of fibre: pure fungicide - 26%; Albit/fungicide – 65%.
Additional treatment: Albit 50 g/hectare+ herbicides based on chlorsulfuron
and quizalofop-p-ethyl. Yield in control was 40.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2004 |
| 184. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
bacteriosis |
48 |
92 |
39 |
42 |
70 |
124,2 |
192 |
108 |
Combination of fungicide with Albit considerably
improved fibre quality: application of halved dose of carboxin/thiram
based fungicide with Albit provided increase of average number of fibre
by 11 units (comparing to application of pure fungicide). Increase of
percent-number of fibre: pure fungicide - 26%; Albit/fungicide – 65%.
Additional treatment: herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-ethyl.
Yield in control was 37.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2004 |
| 185. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
bacteriosis |
41 |
93 |
31 |
35 |
- |
- |
227 |
113 |
Germination: in control - 53%, in variant
with thiram/carboxin-based fungicide – 56%, in variant with combination
of the fungicide and Albit – 60%. Yield in control was 25.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2005 |
| 186. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
bacteriosis |
41 |
93 |
40 |
43 |
- |
- |
227 |
108 |
Germination: in control - 53%, in variant
with thiram/carboxin-based fungicide – 56%, in variant with combination
of the fungicide and Albit – 60%. Additional treatment: benomyl 1 kg/hectare+
herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-ethyl. Yield in control
was 35.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2005 |
| 187. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
bacteriosis |
41 |
93 |
42 |
46 |
- |
- |
227 |
110 |
Germination: in control - 53%, in variant
with thiram/carboxin-based fungicide – 56%, in variant with combination
of the fungicide and Albit – 60%. Additional treatment: Albit 50 g/hectare+
herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-ethyl. Yield in control
was 36.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2005 |
| 188. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
bacteriosis |
41 |
93 |
37 |
41 |
- |
- |
227 |
111 |
Germination: in control - 53%, in variant
with thiram/carboxin-based fungicide – 56%, in variant with combination
of the fungicide and Albit – 60%. Additional treatment: herbicides based
on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-ethyl. Yield in control was 32.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2005 |
| 189. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 ml/tonne |
flax |
bacteriosis |
33 |
73 |
30 |
33 |
- |
- |
221 |
110 |
Germination: in control - 48%, in variant
with carboxin/thiram/carboxin-based fungicide – 51%, in variant with
combination of the fungicide and Albit – 55%. Yield in control was 21.0
centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2006 |
| 190. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 ml/tonne |
flax |
bacteriosis |
33 |
73 |
40 |
43 |
- |
- |
221 |
108 |
Germination: in control - 48%, in variant
with carboxin/thiram/carboxin-based fungicide – 51%, in variant with
combination of the fungicide and Albit – 55%. Additional treatment: benomyl
1 kg/hectare+ herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-ethyl.
Yield in control was 32.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2006 |
| 191. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 ml/tonne |
flax |
bacteriosis |
33 |
73 |
42 |
45 |
- |
- |
221 |
107 |
Germination: in control - 48%, in variant
with carboxin/thiram/carboxin-based fungicide – 51%, in variant with
combination of the fungicide and Albit – 55%. Additional treatment: Albit
50 g/hectare + herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-ethyl.
Yield in control was 34.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2006 |
| 192. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 ml/tonne |
flax |
bacteriosis |
33 |
73 |
34 |
40 |
- |
- |
221 |
118 |
Germination: in control - 48%, in variant
with carboxin/thiram/carboxin-based fungicide – 51%, in variant with
combination of the fungicide and Albit – 55%. Additional treatment: herbicides
based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-ethyl. Yield in control was 30.0
centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2006 |
| 193. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
70 g/tonne |
flax |
ozoniosis |
89 |
89 |
28 |
29 |
- |
- |
100 |
104 |
Yield in control was 22.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2002 |
| 194. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
70 g/tonne |
flax |
ozoniosis |
89 |
89 |
30 |
31 |
- |
- |
100 |
103 |
Additional treatment: Benomyl-based fungicide
+ herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-tefuryl. Yield in
control was 27.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2002 |
| 195. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
70 g/tonne |
flax |
ozoniosis |
89 |
89 |
31 |
34 |
- |
- |
100 |
110 |
Additional treatment: Albit 50 g/hectare
+ herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-tefuryl. Yield in
control was 26.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2002 |
| 196. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
70 g/tonne |
flax |
ozoniosis |
89 |
89 |
34 |
35 |
- |
- |
100 |
103 |
Additional treatment: Albit 50 g/hectare+
benomyl-based fungicide + herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-tefuryl.
Yield in control was 29.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2002 |
| 197. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
70 g/tonne |
flax |
ozoniosis |
89 |
89 |
28 |
29 |
- |
- |
100 |
104 |
Additional treatment: Albit 50 g/hectare.
Yield in control was 23.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2002 |
| 198. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
70 g/tonne |
flax |
ozoniosis |
89 |
89 |
30 |
32 |
- |
- |
100 |
107 |
Additional treatment: Albit 50 g/hectare
+ herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-tefuryl. Yield in
control was 25.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2002 |
| 199. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
ozoniosis |
87 |
93 |
41 |
45 |
- |
- |
107 |
110 |
Yield in control was 37.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2003 |
| 200. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
ozoniosis |
87 |
93 |
47 |
49 |
- |
- |
107 |
104 |
Additional treatment: Benomyl-based fungicide
+ herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-tefuryl. Yield in
control was 45.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2003 |
| 201. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
ozoniosis |
87 |
93 |
49 |
52 |
- |
- |
107 |
106 |
Additional treatment: Albit 50 g/hectare
+ herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-tefuryl. Yield in
control was 46.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2003 |
| 202. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
ozoniosis |
87 |
93 |
45 |
47 |
- |
- |
107 |
104 |
Additional treatment: Albit 50 g/hectare
+ herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-tefuryl. Yield in
control was 40.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2003 |
| 203. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
ozoniosis |
92 |
97 |
33 |
38 |
57 |
127,2 |
105 |
115 |
Combination of fungicide with Albit considerably
improved fibre quality: application of halved dose of carboxin/thiram
based fungicide with Albit provided increase of average number of fibre
by 11 units (comparing to application of pure fungicide). Increase of
percent-number of fibre: pure fungicide - 26%; Albit/fungicide – 65%.
Yield in control was 29.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2004 |
| 204. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
ozoniosis |
92 |
97 |
41 |
44 |
72,2 |
126,4 |
105 |
107 |
Combination of fungicide with Albit considerably
improved fibre quality: application of halved dose of carboxin/thiram
based fungicide with Albit provided increase of average number of fibre
by 11 units (comparing to application of pure fungicide). Increase of
percent-number of fibre: pure fungicide - 26%; Albit/fungicide – 65%.
Additional treatment: benomyl-based fungicide + herbicides based on chlorsulfuron
and quizalofop-p-ethyl. Yield in control was 38.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2004 |
| 205. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
ozoniosis |
92 |
97 |
43 |
48 |
78 |
154 |
105 |
112 |
Combination of fungicide with Albit considerably
improved fibre quality: application of halved dose of carboxin/thiram
based fungicide with Albit provided increase of average number of fibre
by 11 units (comparing to application of pure fungicide). Increase of
percent-number of fibre: pure fungicide - 26%; Albit/fungicide – 65%.
Additional treatment: Albit 50 g/hectare+ herbicides based on chlorsulfuron
and quizalofop-p-ethyl. Yield in control was 40.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2004 |
| 206. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
ozoniosis |
92 |
97 |
39 |
42 |
70 |
124,2 |
105 |
108 |
Combination of fungicide with Albit considerably
improved fibre quality: application of halved dose of carboxin/thiram
based fungicide with Albit provided increase of average number of fibre
by 11 units (comparing to application of pure fungicide). Increase of
percent-number of fibre: pure fungicide - 26%; Albit/fungicide – 65%.
Additional treatment: herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-ethyl.
Yield in control was 37.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2004 |
| 207. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
ozoniosis |
85 |
89 |
31 |
35 |
- |
- |
105 |
113 |
Germination: in control - 53%, in variant
with thiram/carboxin-based fungicide – 56%, in variant with combination
of the fungicide and Albit – 60%. Yield in control was 25.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2005 |
| 208. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
ozoniosis |
85 |
89 |
40 |
43 |
- |
- |
105 |
108 |
Germination: in control - 53%, in variant
with thiram/carboxin-based fungicide – 56%, in variant with combination
of the fungicide and Albit – 60%. Additional treatment: benomyl 1 kg/hectare+
herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-ethyl. Yield in control
was 35.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2005 |
| 209. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
ozoniosis |
85 |
89 |
42 |
46 |
- |
- |
105 |
110 |
Germination: in control - 53%, in variant
with thiram/carboxin-based fungicide – 56%, in variant with combination
of the fungicide and Albit – 60%. Additional treatment: Albit 50 g/hectare+
herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-ethyl. Yield in control
was 36.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2005 |
| 210. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
ozoniosis |
85 |
89 |
37 |
41 |
- |
- |
105 |
111 |
Germination: in control - 53%, in variant
with thiram/carboxin-based fungicide – 56%, in variant with combination
of the fungicide and Albit – 60%. Additional treatment: herbicides based
on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-ethyl. Yield in control was 32.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2005 |
| 211. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 ml/tonne |
flax |
ozoniosis |
85 |
90 |
30 |
33 |
- |
- |
106 |
110 |
Germination: in control - 48%, in variant
with carboxin/thiram/carboxin-based fungicide – 51%, in variant with
combination of the fungicide and Albit – 55%. Yield in control was 21.0
centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2006 |
| 212. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 ml/tonne |
flax |
ozoniosis |
85 |
90 |
40 |
43 |
- |
- |
106 |
108 |
Germination: in control - 48%, in variant
with carboxin/thiram/carboxin-based fungicide – 51%, in variant with
combination of the fungicide and Albit – 55%. Additional treatment: benomyl
1 kg/hectare+ herbicides (potassium salt of chlorosulfuron + quizalofop-P-ethyl).
Yield in control was 32.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2006 |
| 213. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 ml/tonne |
flax |
ozoniosis |
85 |
90 |
42 |
45 |
- |
- |
106 |
107 |
Germination: in control - 48%, in variant
with carboxin/thiram/carboxin-based fungicide – 51%, in variant with
combination of the fungicide and Albit – 55%. Additional treatment: Albit
50 g/hectare + herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-ethyl.
Yield in control was 34.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2006 |
| 214. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 ml/tonne |
flax |
ozoniosis |
85 |
90 |
34 |
40 |
- |
- |
106 |
118 |
Germination: in control - 48%, in variant
with carboxin/thiram/carboxin-based fungicide – 51%, in variant with
combination of the fungicide and Albit – 55%. Additional treatment: herbicides
based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-ethyl. Yield in control was 30.0
centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2006 |
| 215. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
pasmo disease |
18 |
21 |
41 |
45 |
- |
- |
117 |
110 |
Yield in control was 37.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2003 |
| 216. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
pasmo disease |
89 |
90 |
47 |
49 |
- |
- |
101 |
104 |
Additional treatment: benomyl-based fungicide
+ herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-tefuryl. Yield in
control was 45.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2003 |
| 217. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
pasmo disease |
89 |
90 |
49 |
52 |
- |
- |
101 |
106 |
Additional treatment: Albit 50 g/hectare
+ herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-tefuryl. Yield in
control was 46.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2003 |
| 218. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
pasmo disease |
34 |
38 |
45 |
47 |
- |
- |
112 |
104 |
Additional treatment: Albit 50 g/hectare
+ herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-tefuryl. Yield in
control was 40.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2003 |
| 219. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
pasmo disease |
10 |
13 |
33 |
38 |
57 |
127,2 |
130 |
115 |
Combination of fungicide with Albit considerably
improved fibre quality: application of halved dose of carboxin/thiram
based fungicide with Albit provided increase of average number of fibre
by 11 units (comparing to application of pure fungicide). Increase of
percent-number of fibre: pure fungicide - 26%; Albit/fungicide – 65%.
Yield in control was 29.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2004 |
| 220. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
pasmo disease |
78 |
84 |
41 |
44 |
72,2 |
126,4 |
108 |
107 |
Combination of fungicide with Albit considerably
improved fibre quality: application of halved dose of carboxin/thiram
based fungicide with Albit provided increase of average number of fibre
by 11 units (comparing to application of pure fungicide). Increase of
percent-number of fibre: pure fungicide - 26%; Albit/fungicide – 65%.
Additional treatment: Benomyl-based fungicide + herbicides based on chlorsulfuron
and quizalofop-p-ethyl. Yield in control was 38.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2004 |
| 221. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
pasmo disease |
74 |
80 |
43 |
48 |
78 |
154 |
108 |
112 |
Combination of fungicide with Albit considerably
improved fibre quality: application of halved dose of carboxin/thiram
based fungicide with Albit provided increase of average number of fibre
by 11 units (comparing to application of pure fungicide). Increase of
percent-number of fibre: pure fungicide - 26%; Albit/fungicide – 65%.
Additional treatment: Albit 50 g/hectare+ herbicides based on chlorsulfuron
and quizalofop-p-ethyl. Yield in control was 40.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2004 |
| 222. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
pasmo disease |
17 |
26 |
39 |
42 |
70 |
124,2 |
153 |
108 |
Combination of fungicide with Albit considerably
improved fibre quality: application of halved dose of carboxin/thiram
based fungicide with Albit provided increase of average number of fibre
by 11 units (comparing to application of pure fungicide). Increase of
percent-number of fibre: pure fungicide - 26%; Albit/fungicide – 65%.
Additional treatment: herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-ethyl.
Yield in control was 37.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2004 |
| 223. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
pasmo disease |
15 |
38 |
31 |
35 |
- |
- |
253 |
113 |
Germination: in control - 53%, in variant
with thiram/carboxin-based fungicide – 56%, in variant with combination
of the fungicide and Albit – 60%. Yield in control was 25.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2005 |
| 224. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
pasmo disease |
75 |
78 |
40 |
43 |
- |
- |
104 |
108 |
Germination: in control - 53%, in variant
with thiram/carboxin-based fungicide – 56%, in variant with combination
of the fungicide and Albit – 60%. Additional treatment: benomyl 1 kg/hectare+
herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-ethyl. Yield in control
was 35.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2005 |
| 225. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
pasmo disease |
73 |
75 |
42 |
46 |
- |
- |
103 |
110 |
Germination: in control - 53%, in variant
with thiram/carboxin-based fungicide – 56%, in variant with combination
of the fungicide and Albit – 60%. Additional treatment: Albit 50 g/hectare+
herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-ethyl. Yield in control
was 36.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2005 |
| 226. |
carboxin + thiram |
2êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
flax |
pasmo disease |
33 |
40 |
37 |
41 |
- |
- |
121 |
111 |
Germination: in control - 53%, in variant
with thiram/carboxin-based fungicide – 56%, in variant with combination
of the fungicide and Albit – 60%. Additional treatment: herbicides based
on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-ethyl. Yield in control was 32.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2005 |
| 227. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 ml/tonne |
flax |
pasmo disease |
21 |
26 |
30 |
33 |
- |
- |
124 |
110 |
Germination: in control - 48%, in variant
with carboxin/thiram/carboxin-based fungicide – 51%, in variant with
combination of the fungicide and Albit – 55%. Yield in control was 21.0
centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2006 |
| 228. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 ml/tonne |
flax |
pasmo disease |
74 |
74 |
40 |
43 |
- |
- |
100 |
108 |
Germination: in control - 48%, in variant
with carboxin/thiram/carboxin-based fungicide – 51%, in variant with
combination of the fungicide and Albit – 55%. Additional treatment: benomyl
1 kg/hectare+ herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-ethyl.
Yield in control was 32.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2006 |
| 229. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 ml/tonne |
flax |
pasmo disease |
74 |
77 |
42 |
45 |
- |
- |
104 |
107 |
Germination: in control - 48%, in variant
with carboxin/thiram/carboxin-based fungicide – 51%, in variant with
combination of the fungicide and Albit – 55%. Additional treatment: Albit
50 g/hectare + herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-ethyl.
Yield in control was 34.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2006 |
| 230. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 ml/tonne |
flax |
pasmo disease |
24 |
26 |
34 |
40 |
- |
- |
108 |
118 |
Germination: in control - 48%, in variant
with carboxin/thiram/carboxin-based fungicide – 51%, in variant with
combination of the fungicide and Albit – 55%. Additional treatment: herbicides
based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-ethyl. Yield in control was 30.0
centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2006 |
| 231. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
winter wheat |
– |
– |
– |
25.8 |
26.2 |
- |
- |
– |
102 |
Var. Pobeda 50. |
Prikumskiy selektsioner LLC, 2004 |
| 232. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 ê g/tonne |
1 ê g/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
winter whe at |
– |
– |
– |
23.3 |
24.5 |
- |
- |
– |
105 |
Var. Pobeda 50. |
Prikumskiy selektsioner LLC, 2004 |
| 233. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
winter wheat |
– |
– |
– |
27.2 |
29.1 |
- |
- |
– |
107 |
Var. Don-95. |
Prikumskiy selektsioner LLC, 2004 |
| 234. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 ê g/tonne |
1 ê g/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
winter whe at |
– |
– |
– |
24 |
26.7 |
- |
- |
– |
111 |
Var. Don-95. |
Prikumskiy selektsioner LLC, 2004 |
| 235. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 ê g/tonne |
1 ê g/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
winter wheat |
– |
– |
– |
26.7 |
28 |
- |
- |
– |
105 |
Var. Donskaya bezostaya |
Prikumskiy selektsioner LLC, 2004 |
| 236. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
winter wheat |
– |
– |
– |
25.5 |
25.4 |
- |
- |
– |
100 |
Var. Donskaya bezostaya . |
Prikumskiy selektsioner LLC, 2004 |
| 237. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
winter wheat |
– |
– |
– |
29.4 |
28.4 |
- |
- |
– |
97 |
Var. Prikumskaya 110 . |
Prikumskiy selektsioner LLC, 2004 |
| 238. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
winter wheat |
– |
– |
– |
27.4 |
28.4 |
- |
- |
– |
104 |
Var. Prikumskaya 110 . |
Prikumskiy selektsioner LLC, 2004 |
| 239. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
winter wheat |
– |
– |
– |
23.5 |
25.1 |
- |
- |
– |
107 |
Var. Prikumchanka . |
Prikumskiy selektsioner LLC, 2004 |
| 240. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
winter wheat |
– |
– |
– |
22.6 |
23.8 |
- |
- |
– |
105 |
Var. Prikumchanka . |
Prikumskiy selektsioner LLC, 2004 |
| 241. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
winter wheat |
– |
– |
– |
27.3 |
29.3 |
- |
- |
– |
107 |
Var. Prikumskaya 124 . |
Prikumskiy selektsioner LLC, 2004 |
| 242. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 g/tonne |
winter wheat |
– |
– |
– |
25.7 |
27.5 |
- |
- |
– |
107 |
Var. Prikumskaya 124 . |
Prikumskiy selektsioner LLC, 2004 |
| 243. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 ml/tonne |
ïðîñî |
head smut |
100 |
100 |
34.4 |
– |
- |
- |
100 |
– |
Trial was performed under artificially
high infectious conditions (92-95% infestation). Combination of carboxin/thiram/carboxin-based
fungicide with Albit increased (comparing to pure fungicide): field germination
by 3-10%, number and weight of seeds from one plant, weight of 1000 seed.
Yield in control was 29.9 centners/hectare. Yield in variant with Albit
(seed treatment, 50 mL/t) was 3.42 t/ha.
|
All-Russia Institute of Leguminous and
Groat Crops, 2002 |
| 244. |
carboxin + thiram |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
50 ml/tonne |
ïðîñî |
head smut |
100 |
100 |
33.2 |
– |
- |
- |
100 |
– |
Trial was performed under artificially
high infectious conditions (92-95% infestation). Yield in control was
30.3 centners/hectare. Yield in variant treated with Albit only (50 ml/tonne)
was 32.8 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Institute of Leguminous and
Groat Crops, 2003 |
| 245. |
benomyl |
1 êã/ãà |
0,5 êã/ãà |
50 ã/ãà |
flax |
anthracnose |
50 |
50 |
27 |
29 |
- |
- |
100 |
107 |
Foliar spraying was carried out jointly
with herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-tefuryl. Yield
in control was 22.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2002 |
| 246. |
benomyl |
1 êã/ãà |
0,5 êã/ãà |
50 ã/ãà |
flax |
anthracnose |
70 |
70 |
30 |
34 |
- |
- |
100 |
113 |
Foliar spraying was carried out jointly
with herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-tefuryl. Seeds
were treated with carboxin/thiram based fungicide. Yield in control was
28.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2002 |
| 247. |
benomyl |
1 êã/ãà |
0,5 êã/ãà |
50 ã/ãà |
flax |
anthracnose |
70 |
60 |
30 |
34 |
- |
- |
86 |
113 |
Foliar spraying was carried out jointly
with herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-tefuryl. Seeds
were treated with Albit 50 g/tonne. Yield in control was 29.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2002 |
| 248. |
benomyl |
1 êã/ãà |
0,5 êã/ãà |
50 ã/ãà |
flax |
anthracnose |
80 |
80 |
31 |
35 |
- |
- |
100 |
113 |
Foliar spraying was carried out jointly
with herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-tefuryl. Seeds
were treated with carboxin/thiram based fungicide + Albit 50 g/tonne.
Yield in control was 29.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2002 |
| 249. |
benomyl |
1 êã/ãà |
0,5 êã/ãà |
50 ã/ãà |
flax |
anthracnose |
70 |
70 |
31 |
36 |
- |
- |
100 |
116 |
Foliar spraying was carried out jointly
with herbicides based on chlorsulfuron and quizalofop-p-tefuryl. Seeds
were treated with Albit 70 g/tonne. Yield in control was 29.0 centners/hectare. |
All-Russia Flax Institute, 2002 |
| 250. |
benomyl |
2 êg/tonne |
1 êg/tonne |
30 ml/hectare |
ïðîñî |
head smut |
100 |
100 |
14.7 |
17 |
7,832 |
19,904 |
100 |
116 |
Germination: in control - 97%, in variant
with carboxin/thiram -based fungicide – 87%, in variant with combination
of the fungicide and Albit – 93%. Application of combination of the fungicide
and Albit increased panicle length by 4.87 cm, weight of 1000 seeds by
0.21 g; application of pure fungicide did not increase these parameters
over control ones. Yield in control was 13.1 centners/hectare. |
Agricultural Scientific Institute of South-East,
2004 |
| 251. |
CuCl 2 3CuO 4H 2O + dimethoate + flutriafol
+ mancozeb + dimethomorph + sulphur + dithianon |
– |
– |
200 ml/hectare |
vine |
downy mildew |
95 |
98 |
– |
– |
- |
- |
103 |
– |
Application rates of fungicides were decreased
twice. Addition of Albit to complex of fungicides suppressed development
of diseases up to 1.5 months. |
All-Russia Institute of Viticulture and
Vine Processing, 2003 |
| 252. |
CuCl 2*3CuO 4H 2O + dimethoate + flutriafol
+ mancozeb + dimethomorph + sulphur + dithianon |
– |
– |
200 ml/hectare |
vine |
powdery mildew |
55 |
84 |
– |
– |
- |
- |
153 |
– |
Application rates of fungicides were decreased
twice. Addition of Albit to complex of fungicides suppressed development
of diseases up to 1.5 months. |
All-Russia Institute of Viticulture and
Vine Processing, 2003 |
According to presented results of the trials, one can conclude, that application
of combination of Albit and reduced dose of pesticide in comparison to full
dose of the pesticide provides better protection of plants against
diseases (by 30% in terms of biological efficiency) and provides
yield increase of 7% while net profit is increased twice (data
on efficiency of seed treatment agents against leaf infections were not taken
into account).
2) It is established, that Albit possesses pronounced immunogenic activity
via inducing natural mechanisms of plant resistance to diseases (systematic
acquired resistance, reaction of hypersensitivity). Due to this activity, Albit
virtually compensates fungicidal activity of chemical pesticide decreased
in result of application rate reduction. Immunization of plants is
able to easily compensate considerable reduction of application rates of many
fungicides, which are (in some cases) quite overrated.
4) High ecological compatibility of Albit is both its advantage and disadvantage.
Since Albit consists of natural metabolites of soil bacteria, it is easily
degraded by saprophyte non-pathogenic microflora living on surface of seeds
and plant leaves (Penicillia, Aspergilli, yeasts, bacteria) and often
do not has enough time to influence on plants properly. Therefore, even small
amount of chemical fungicide, applied together with Albit, suppresses
activity of microflora and protects Albit from degradation, that visibly
increases Albit’s efficiency. Chemical fungicide acts in this case as a preservative.
It is the reason why combinations of Albit with fungicides below 50% of their
recommended application rate are quite effective sometimes.
For example, in trials carried out by Institute of Biochemistry and Physiology
of Microorganisms (2004) on spring barley, addition of even 10% of recommended
dose of fungicides suppressed development of pathogenic microflora and increased
biological efficiency of Albit against root rots from 36 to 100%. In field trials
carried out by All-Russia Institute of Leguminous and Groat Crops on spring barley
(2005), presowing seed treatment with combination of Albit and 13% of recommended
dose of thiabendazole/flutriafol – based fungicide, provided yield increase of
32% over control, whereas treatment with full dose of the fungicide provided
just 14% of yield increase; treatment with Albit only provided 11% of yield increase.
Both Albit/fungicide and fungicide only treatments provided 100% protection from
root rots of barley, but Albit/fungicide treated plants demonstrated visibly
accelerated growth, see in details here.
Fig. 18. Schematic description of mutual reinforcement of jointly used Albit
and chemical fungicides.
In some cases, when decrease of fungicide application rate is undesirable
(smut infection, epiphytotic development of diseases, etc.), Albit might be
used in combination with full application rate of fungicide.
Such treatment relives stress caused by fungicides, that notably increases
yield while fungicidal activity remains intact. However, even in this case
one can use the minimum recommended rate.
Table 3. Results of field trials on combined application of Albit with full
doses of fungicides and seed protectants
Albit Scientific and Industrial LLC managed to establish a partnership with
regional dealers of leading agrochemical companies (Avgust, BASF, Syngenta,
SAHO, Agrorus) in many regions of Russia. In the beginning, dealers were quite
hostile to possibility of joint application of Albit with reduced rates of
their chemical fungicides, but then they receive evidences, that possibility
to combine chemicals with Albit, on the contrary, increases sales of chemicals.
Farms that were too poor to buy full assortment of chemicals, now are buying
minimal (and then increasing) amounts of chemicals to use them with Albit,
that results in increase of total amounts of chemical fungicides sold. New
resistant pathogenic strains of microorganisms were not detected in soil on
fields, where Albit was applied with chemical products. Additionally, the phytosanitary
situation of soil even improves, soil becomes healthier according to data of
Ryazan’ and Saratov regional Plant Protection Stations.
By now, there are many examples of successful application
of fungicide and plant growth stimulator combinations in agricultural practice.
For example, addition of plant growth regulators to carboxin/thiram – based
fungicide Vitavaks 200 lead to creation of new fungicidal seed treatment
agent Vitavaks 200 FF which possesses additional plant growth stimulating effect.
Possibly, producers of chemical pesticides should review inclusion of Albit
into preparative forms of chemicals in manufacturing stage,
that would simplify application technology of well reputated mixtures.
It is necessary to note in conclusion, that application of decreased rates
of chemical fungicides has become a wide spread agricultural technique in the
most agriculturally advanced regions of Russia (Krasnodar krai, Belgorod oblast,
republics of Tatarstan and Bashkortostan, etc.). Also, in countries of European
Union farmers are additionally subsidized to decrease fungicidal load on fields.
Analogous arrangements on decrease consumption of chemical fungicides are undertaken
by governments of USA, Japan, Brazil, Canada, Australia and New Zealand. It
is steady progressive tendency in world agriculture, which
can be successfully realized with application of Albit.
Basing on data of long-term trials, All-Russia Institute of Biological Protection
recommended to use plant growth regulators (including Albit) in combination
with halved doses of chemical seed treatment agents and fungicides for protection
of crops from main diseases. Analogous recommendations were issued by All-Russia
Institute of Plant Protection, Flax Institute, and other institutes.